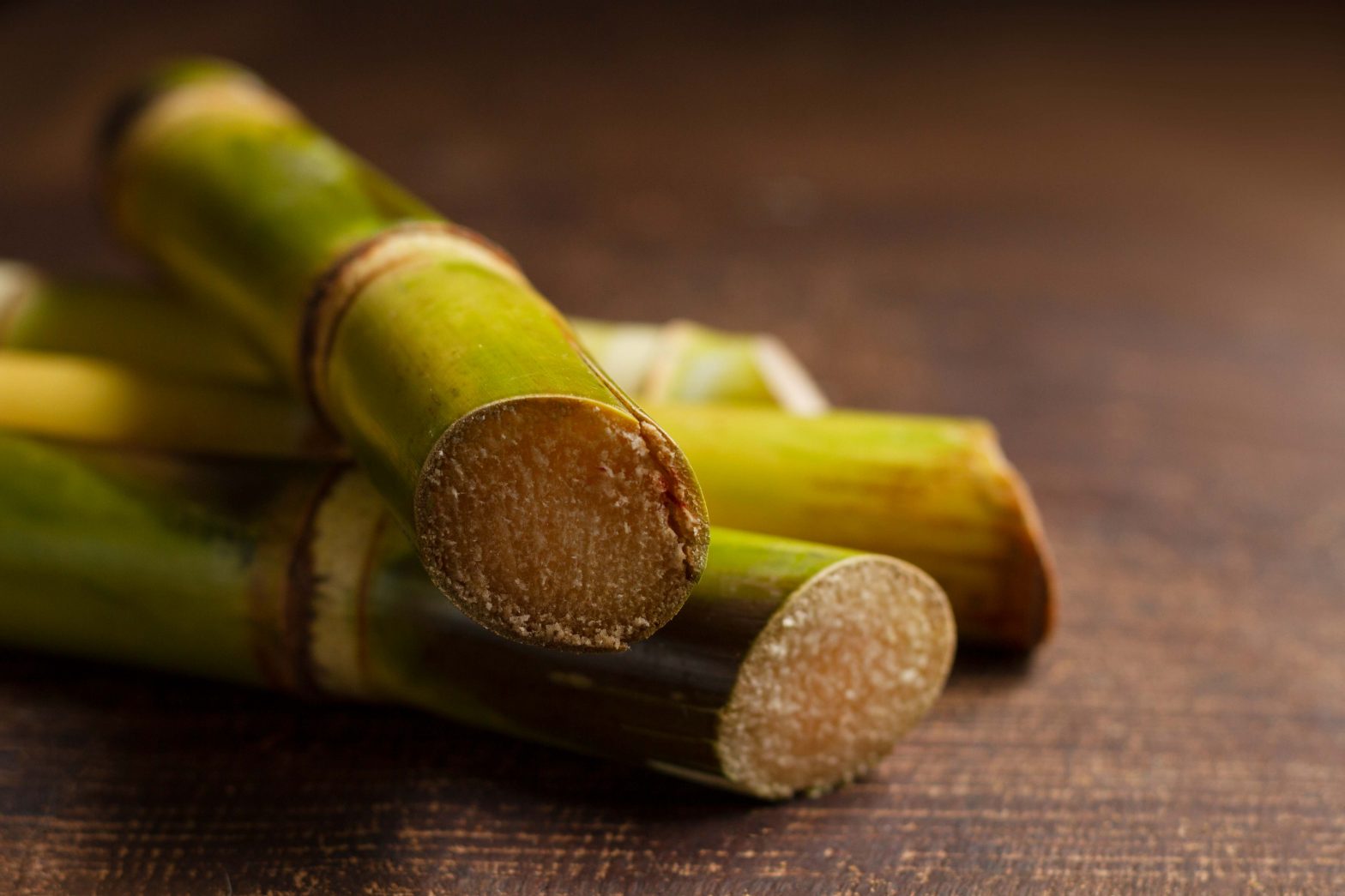
India, the world’s second-largest sugarcane producer is about to witness a sharp rise in sugarcane production this year, thanks to the unseasonal monsoon that has helped the millers increase their yield per hectare.
The production has been expected to reach 305 lakh tonnes in 2024 from 291.50 tonnes(1) in 2023. The surge was particularly observed in Ahmednagar, Marathwada, and Solapur in Maharashtra and the northern belt of Karnataka.
Despite increased yield in the two major sugarcane-producing states in India, there is a huge scope for increasing the yield per hectare in the sub-tropical regions of India. Several constraints such as long winters, low sunshine hours, water logging, imbalance use of fertilizer, and low-quality seeds(2) lead to a decline in the overall production of sugarcane in subtropical regions of the country. One major factor for lower productivity is the growth of fungus diseases.
Sugarcane plants witness substantial damage
As per agriculture experts, sugarcane plants witness substantial damage due to more than 100 fungi diseases globally(3), leading to an overall reduction in yields. Red Rot in sugarcane is one of the most common fungus diseases that damage yield, however, very few know about the deadly Whip smut fungi of sugarcane.
Sugarcane smut, also known as caulicolous is caused by the fungus called ‘Sporisorium scitamineum,’ which can be identified as black or grey growth referred to as “whip smut” on the plant. The disease has been categorized as the most serious fungi infection that has the capability of stunting growth, and damaging the quality and quantity of sugarcane plants if they remain untreated.
Leads to complete crop failure
Under its favorable conditions, it can also lead to complete crop failure. Moreover, it has the potential to reduce the juice quality of the sugarcane crops. Sugarcane plants in dry climatic conditions are more prone to smut fungus as the fungus spreads in hot climates. Whereas, the wetter climatic conditions reduce its teliospore longevity resisting its growth.(4)
Sub-tropical regions require extra measures(5) when it comes to preventing plant diseases like whip smut due to their high-temperature disparity, which increases the instance of diseases and pests in the sugarcane plants.
Experts advise a well-planned Integrated Disease Management (IDM) Strategy to prevent and cure the sugarcane crop from these fungus diseases, which includes removing infected plants, using treated seeds, and applying high-quality fungicides.
Conclusion
AgFarm’s fungicide Relevant (Azoxystrobin 18.2% w/w + Difenoconazole 11.4% w/w SC), a broad-spectrum fungicide, has been highly effective against fungus diseases such as Leaf Spot, Blast, Sheath Blight, Red Rot, Early and Late Blight, Rust, Powdery Mildew, Purple Blotch, and Leaf Blotch, among others.
Regular monitoring of plants along with the application of fungicides not only eradicates the fungus but also minimizes the risk of future infestation by protecting early-stage infestation. With the right disease management in the dry regions of the country, the yield of sugarcane plants can be increased in the other states and would eventually surge the overall sugarcane production of the country.
Reference:-
- https://indianexpress.com/article/cities/pune/indias-sugar-sector-upbeat-as-maharashtra-karnataka-report-increase-in-cane-yield-sugar-production-9084473/
- https://www.nfsm.gov.in/BriefNote/BN_Sugarcane.pdf
- https://www.ikisan.com/ap-sugarcane-disease-management.html#:~:text=Red%20rot%20is%20one%20of,in%20Bihar%20and%20Uttar%20Pradesh.
- https://apsjournals.apsnet.org/doi/10.1094/PHYTO-05-21-0221-RVW
- https://www.nfsm.gov.in/BriefNote/BN_Sugarcane.pdf